Securing Your Smart Stuff: How To Use SSH With IoT Devices
Connecting to your smart devices, the ones that make up the Internet of Things (IoT), can feel a bit like reaching out to something far away. You want to make sure that connection is safe and sound, especially when you are sending commands or checking on things. This is where using ssh iot device methods comes into play, offering a solid way to keep your interactions private and protected. It's about making sure only you, or those you trust, can talk to your little gadgets, whether they are in your home or out in the wild.
Many folks are getting more and more interested in how to manage their smart home gear or industrial sensors without being right next to them. You might have a tiny computer, like a Raspberry Pi, doing a job somewhere, and you need to peek at its files or run an update. Using SSH, which stands for Secure Shell, gives you that kind of remote access, and it does so with a good amount of security built right in. It's a standard tool, widely trusted, and for good reason, too.
This conversation will walk through why SSH is such a big deal for your IoT setup, how you can get it working, and some common bumps you might hit along the way. We will also look at how to keep your SSH connections strong and safe, so you can manage your devices with peace of mind. You know, it's pretty much a must-have skill if you're playing with IoT these days, and honestly, it's not as tricky as it might sound, especially once you get the hang of it.
- Malia Obama Boyfriend
- Mayme Hatcher
- How Did Thomas Massie Wife Pass
- Two Babies One Fox Comic Original
- Lexiscandyshop
Table of Contents
- The Core Idea: Why SSH Matters for Your IoT Gear
- Setting Up SSH on Your IoT Device: A Practical Look
- Common SSH Hurdles with IoT and How to Clear Them
- Keeping Your IoT SSH Setup Strong and Secure
- Frequently Asked Questions About SSH and IoT Devices
- Wrapping Things Up
The Core Idea: Why SSH Matters for Your IoT Gear
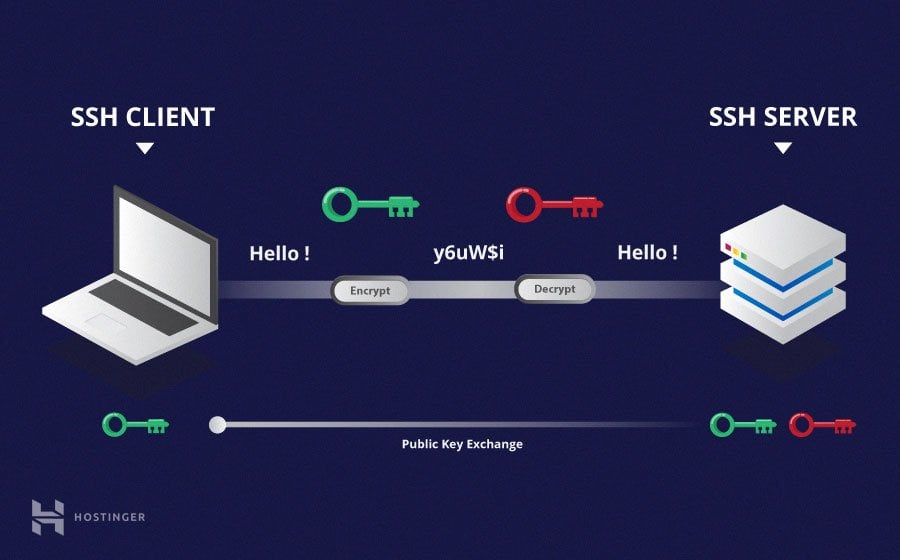
When you have a small computer, like a smart thermostat or a sensor out in a field, it needs a way to communicate with you. Sometimes, you need to tell it what to do, or perhaps get some data back from it. This is where remote access comes in, and for many, SSH is the go-to choice. It's a method that lets you connect to a device over a network, and it does so in a way that keeps things private and stops others from listening in. That, in a way, is the whole point.
Think about it: your smart door lock or your garden watering system might be connected to the internet. You wouldn't want just anyone to be able to get in and mess with them, would you? SSH gives you a private, encrypted tunnel to your device. This means all the information going back and forth is scrambled, so prying eyes cannot easily read it. It's a pretty big deal for keeping your personal space, and your data, safe. So, it's not just about getting access; it's about getting *secure* access.
Keeping Things Safe and Sound
One of the main reasons people choose SSH for their IoT devices is for security. It's built to protect your connection from many common attacks. For example, if someone tries to listen in on your connection, they will just hear gibberish because of the encryption. This helps keep your commands, your passwords, and any data your device sends back to you private. In some respects, it's like having a secret handshake that only your device and your computer know.
- Princess Qajar
- Bonnie Blue 1000 People Challenge
- Pepper0
- Camilla Araujo Onlyfans Video Name List 2025
- Xvideos
The system also checks to make sure you are talking to the right device, and that the device is talking to the right you. This is done using something called "host keys," which we will talk about a little more later. Using SSH, every host has a key, and clients remember the host key associated with a particular connection. This helps stop someone from pretending to be your device. It's a very good layer of protection, especially for things that might be left unattended for long periods, like a remote weather station.
Getting to Your Devices from Anywhere
Beyond security, SSH offers amazing flexibility. You can be miles away, perhaps on vacation, and still check on your smart home or reboot a remote sensor. All you need is an internet connection and the right tools on your computer. This means you do not have to physically go to each device every time you need to make a small change or check its status. That, honestly, saves a lot of time and effort.
For instance, if you have a Raspberry Pi acting as a home automation hub, you might need to update its software or adjust a setting. Instead of pulling it out from behind the TV and plugging in a keyboard and screen, you can just open up a terminal on your laptop and connect right in. It's like having a direct line to your device's brain, no matter where you are. This convenience is a huge part of why SSH is so popular for managing iot devices, as a matter of fact.
Setting Up SSH on Your IoT Device: A Practical Look
Getting SSH up and running on your IoT device usually involves a few straightforward steps. Most small Linux-based devices, like Raspberry Pis or many custom boards, come with SSH capabilities built in or are easy to add. The process often involves enabling the SSH server on the device itself and then using an SSH client on your computer to connect. It's not too different from connecting to any other server, really.
For example, if you are setting up a new device, you might need to enable SSH through a configuration tool or by editing a specific file. Once that is done, your computer, running an SSH client like OpenSSH (common on Linux and macOS, and available on Windows through PowerShell) or PuTTY (a popular choice for Windows users), can start the connection. You just tell it the device's address and your username, and away you go. That, typically, is how it starts.
Generating and Using SSH Keys
While you can use a password to log in via SSH, the much more secure and recommended way is to use SSH keys. These are like a very long, very complex password split into two parts: a public key and a private key. You put the public key on your IoT device, and you keep the private key safe on your computer. When you try to connect, your computer uses the private key to prove it is you, and the device checks it against the public key it has. This is a much stronger method than passwords alone, honestly.
If you are using OpenSSH, you can generate these keys with a simple command. Then, you copy the public key to your IoT device's authorized_keys file. Add identity using keychain as @dennis points out in the comments, to persist the key, meaning you do not have to type in your private key's passphrase every single time you connect. This makes for a much smoother and more secure workflow. It's a bit of setup at the start, but it pays off big time in security and convenience, you know.
Handling Connection Drops and Idle Sessions
Sometimes, when you are connected to an IoT device via SSH, especially if you leave the session open for a while without doing anything, it might just disconnect. A PuTTY session left idle will disconnect at a time determined by the host server, or even your local network. This can be pretty annoying, especially if you are in the middle of something important. It's a common issue, and thankfully, there are ways to manage it.
One way to keep your connection alive is to configure your SSH client to send "keepalive" messages. This causes PuTTY to send null SSH packets to the remote host at regular intervals. These are tiny, harmless packets that just tell the server, "Hey, I am still here!" This tricks the server into thinking the session is active, preventing it from timing out and closing your connection. It's a simple fix that makes a big difference for long-running tasks, and it's something you will probably want to set up right away, more or less.
Making SSH Config Files Work for You
If you are connecting to multiple IoT devices, or if your devices have unusual port numbers or specific settings, typing out long SSH commands every time can get tiresome. This is where an SSH config file becomes incredibly useful. It lets you save all those specific details for each device under a simple nickname. For example, you can tell your computer: "When I type 'ssh my_iot_sensor', connect to this specific IP address, using this username, and this port."
For Windows users using OpenSSH through PowerShell, or for Linux and macOS users, you can edit or create the file now by typing a command that opens it in a text editor. Inside, you can define entries like: `Host github.com hostname ssh.github.com port 443`. This means you can just type `ssh github.com` and it will use those settings. This variable sounds like what I am looking for, but it is not defined, can sometimes happen if you are trying to use a variable within the config file that is not standard, but for basic host definitions, it is quite straightforward. It really streamlines your connection process, making it faster and less prone to typos, honestly.
Common SSH Hurdles with IoT and How to Clear Them
Even with the best intentions, you might run into a few snags when trying to SSH into your IoT devices. It happens to everyone, and often the solutions are simpler than they seem. For whatever reason, this is proving to be impossible and I haven't the slightest clue why, is a common feeling when you are troubleshooting SSH for the first time. But with a bit of patience and knowing where to look, you can usually sort things out. It's all part of the learning process, you know.
These issues can range from simple typos in your commands to more complex network settings or key problems. The key is to break down the problem into smaller pieces and check each one. Is the device on? Is it connected to the network? Is the SSH server running on the device? These basic checks can save you a lot of headache. So, let's look at some common ones.
When Connections Just Won't Happen
One of the most frustrating things is when you try to connect and nothing happens, or you get an error message. When I try to ssh into my server with user@hostname, I get an error, is a very common starting point for troubleshooting. This could mean a few things. Perhaps the device is not reachable on the network, or the SSH server on the device is not running. It could also be a firewall blocking the connection, either on your computer or on the device itself.
Another common scenario is an issue with your SSH keys. After installing Git on my new work computer, generating my SSH key and adding it on GitLab, I'm trying to clone a project but I get the following error. This suggests a problem with the key itself or how it is being used. Double-check that your public key is correctly placed on the IoT device and that your private key is accessible and has the right permissions on your computer. Sometimes, it's just a simple typo in the username or hostname, too.
Sorting Out X11 Forwarding
Some advanced uses of SSH involve forwarding graphical applications from your IoT device to your computer's screen. This is called X11 forwarding. If you run SSH and display is not set, it means SSH is not forwarding the X11 connection. This can be confusing if you expect a graphical window to pop up and nothing does. It's a specific setting you need to enable.
To confirm that SSH is forwarding X11, check for a line containing "requesting x11 forwarding" in the output of your SSH client when you connect. If it is not there, you might need to enable it in your SSH client settings or by adding the `-X` flag to your SSH command. Also, make sure your IoT device's SSH server is configured to allow X11 forwarding. It's a neat feature for running lightweight graphical tools on your remote devices, but it needs to be set up just right, you know.
Dealing with Host Key Warnings
When you connect to an SSH server for the first time, your SSH client will usually show you a "host key fingerprint" and ask if you want to accept it. This is a security measure. Using SSH, every host has a key, and clients remember the host key associated with a particular connection. If that key ever changes unexpectedly, your client will warn you. This is a good thing, as it could mean someone is trying to trick you into connecting to a different, malicious server.
However, sometimes host keys genuinely change, like if you reinstall the operating system on your IoT device. In such cases, your SSH client will complain, saying the host key has changed. You will need to remove the old host key from your computer's known_hosts file before you can connect again. It's a bit of a manual step, but it is there to protect you. Just be sure you know why the key changed before you accept a new one, as a matter of fact.
Keeping Your IoT SSH Setup Strong and Secure
Once you have SSH working with your IoT devices, the job is not completely done. You need to keep things secure over time. This means following some best practices to make sure your remote access remains a safe pathway and not an open door for unwanted guests. It's about ongoing vigilance, you know, because threats can change.
The goal is to make it as hard as possible for anyone who is not you to get into your devices. This involves more than just setting up SSH; it involves how you use it and how you maintain your devices. So, let's talk about some key habits that will help keep your IoT world secure.
Beyond Passwords: Always Use Keys
We touched on this earlier, but it is worth saying again: avoid password-only authentication for SSH on your IoT devices whenever possible. There is no public private key authentication, the user and the password are in the script, is a real security risk, as passwords can be guessed or brute-forced. SSH keys are vastly more secure. They are much longer and more complex than any password you could reasonably type or remember, making them incredibly difficult to crack.
Make sure you use a strong passphrase for your private SSH key, too. This adds another layer of protection, so even if someone gets hold of your private key file, they cannot use it without the passphrase. Add identity using keychain as @dennis points out in the comments, to persist, which helps manage these passphrases, so you do not have to type them repeatedly. This makes key-based authentication both secure and convenient, which is a really nice combination, honestly.
Regular Checks and Updates
Just like any other piece of software, the SSH server and client on your devices and computer need to be kept up to date. Software updates often include security fixes for newly discovered vulnerabilities. Running old versions of software can leave your devices open to attacks. So, make it a habit to check for and apply updates regularly to both your IoT devices and the computer you use to connect to them. This is a pretty simple step that makes a huge difference in security.
Also, periodically review who has access to your IoT devices via SSH. If someone no longer needs access, remove their public key from the device. If you suspect a private key has been compromised, generate a new one and remove the old one from all your devices. It's about staying on top of things, keeping your digital garden tidy, so to speak. This kind of proactive approach helps keep your ssh iot device connections safe for the long haul, you know.
Frequently Asked Questions About SSH and IoT Devices
Here are some common questions people often have about using SSH with their smart devices:
Why use SSH for IoT devices?
You use SSH for IoT devices mainly for secure remote access. It encrypts your connection, keeping your commands and data private, and it helps make sure you are connecting to the correct device. This is crucial for managing devices that might be in hard-to-reach places or that handle sensitive information, so it's a pretty important tool.
How do I secure SSH on my IoT device?
To secure SSH on your IoT device, always use SSH key-based authentication instead of passwords. Make sure your private keys have strong passphrases. Also, keep your device's operating system and SSH software updated, and disable root login. You might also consider changing the default SSH port, and limiting who can connect from which IP addresses, which can add another layer of protection, you know.
What if my SSH connection to an IoT device keeps dropping?
If your SSH connection keeps dropping, it is often due to idle timeouts. You can configure your SSH client, like PuTTY or OpenSSH, to send "keepalive" packets. This causes PuTTY to send null SSH packets to the remote host at regular intervals, which helps prevent the connection from timing out. Network instability or firewalls can also cause drops, so checking those areas might help too, honestly.
Wrapping Things Up
Using SSH for your IoT devices is a really smart move for both security and convenience. We have talked about how it helps keep your connections private and lets you manage your gadgets from anywhere. We have also looked at setting it up, from using SSH keys to making your config files work for you. And we covered some common problems, like connections that just won't happen or dealing with host key warnings. You know, things like checking for a line containing "requesting x11 forwarding" can really help confirm what's going on.
Remember, the world of IoT is always growing, and keeping your devices safe is a continuous effort. Sticking with SSH keys, keeping your software updated, and being mindful of your network setup will go a long way. This causes PuTTY to send null SSH packets to the remote host, which is a small but effective trick for keeping sessions alive. By putting these ideas into practice, you can feel much more confident about your smart setup. For more detailed information on SSH security, you might want to check out resources like SSH.com's protocol guide. It's all about making your digital life a bit smoother and a lot safer, honestly.
- Meadow Sisto
- Ymaalcom
- Corinna Kopf Fapello
- What Happened To Frankie Katafias
- Sotwe If%C5%9Falar Gujarati Movie Download
SSH Tutorial: What is SSH, Encryptions and Ports

What Is SSH? | How to Use SSH (Secure Shell) | Gcore

What is a Secure Shell Protocol (SSH)? Everything to Know